What is cellulose acetate?
Cellulose acetate is reacted from cellulose and acetic anhydride, in condition of catalyst and other additives. With acetic acid as solvent, the process of cellulose basically is heterogeneous reaction.
According to the degree of substitution(DS), Cellulose acetate can be commonly classified to cellulose diacetate(DAC) and cellulose triacetate(TAC). Usually, DAC has DS with 2.2-2.5 while TAC has DS with above 2.7.(DS is an average number, It represents the number of –OH which is substituted by –C0CH3)
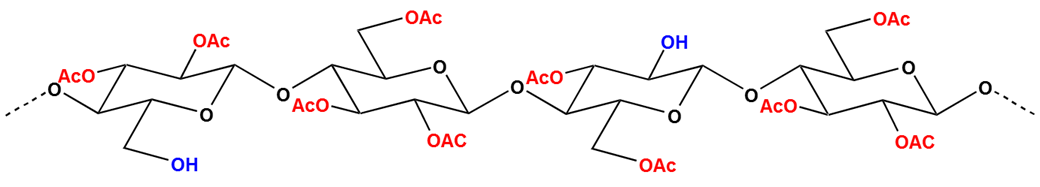 The molecular structure of cellulose acetate
The molecular structure of cellulose acetate
Push Acetati can produce various kinds of product with different application, specification and properties(Include different viscosity/degree of polymerization, DS, clarity etc.) to meet the individual requirement of the customer.
Made with nature in mind
Cellulose acetate is an eco-friendly material that is manufactured from cellulose, a natural raw material obtained from well-managed forests that are conscientiously harvested and replanted with future generations in mind.
Furthermore, the process of cellulose acetate is carefully optimized towards reducing environmental impact at every stage by recovering and reusing solvent, water and energy and limiting the use of chemicals to the very minimum.
To learn more about the raw material of cellulose acetate>>>>
Biodegradability of cellulose acetate
Cellulose acetate is a kind of environmentally friendly products and much more biodegradable than aromatic polyesters and polypropylene.
Degradation of production is also a factor of sustainability. As for cellulose acetate, the degradation process can be generally divided into two steps:
1.First step, the removal of acetyl groups;
2. Then, the breakdown of the remaining cellulosic structures occurs.
To learn more about the biodergrability of cellulose acetate>>>> Solubility of cellulose acetate Usually, the solubility of cellulose acetate depends on the average degree of substitution, the distribution of substituents along the chain and the distribution on the primary and secondary –OH groups. The higher combined acetic acid, the poorer solubility. Compared with other cellulose ester such as nitrocellulose, viscose cellulose, ethyl cellulose, etc., The solubility of cellulose acetate is poorer. It can be dissolved by only a few solvent. Thanks to this property, the chemical resistance is superior. The typical solvent for cellulose triacetate is dichloromethane and the typical solvent for cellulose diacetate is acetone.
Solvent Good Solubility Poor Solubility Esters
Ethyl acetate
〇
Butyl acetate
〇
Ethyl lactate
〇
2-Ethoxyethyl acetate
〇
Ketones
Acetone
〇
Methyl ethyl ketone
〇
Methyl isobutyl ketone
〇
Cyclohexanone
〇
Cyclic ethers
1,4-Dioxane
〇
Tetrahydrofuran
〇
Glycols
Ethylene glycol
〇
Ethylene glycol acetate
〇
Hexylene glycol
〇
Aromatics
Toluene, xylene
〇
Aliphatics
Hexane, Heptane, ...
〇
Cyclohexane
〇
Alcohols
Ethanol
〇
Iso-Propanol
〇
Diacetone alcohol
〇
2-Methoxyethanol
〇
Others
Dimethyl formamide
〇
Dimethyl sulfoxide
〇
Methylene chloride
〇
Chloroform
〇
1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone
〇
Mixtures of Esters & Alcohols
Ethyl acetate / Ethanol, 75/25
〇
Ethyl acetate / Ethanol, 50/50
〇
Ethyl acetate / Ethanol, 30/70
〇


